Double Dimension Array (Matrix Sum)
As we have learned about array in our previous articles. Here by will go through the example of Double Dimension Array. We have demonstrated Array of Rows and Columns for Matrix. We have used #define R and C for number of rows and columns as a constant. (Macro)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define R 3
#define C 3
void main()
{
int mat[R][C]; //To Store Matrix
int rowtotal[R]; //To Store Total of Each Row
int columntotal[C];//To Store Toatl of Each Column
int i,j; // for loop
clrscr();
//Initalized Row and Columns Total to Zero
for(i=0;i<R;i++)
{
rowtotal[i]=0;
}
for(i=0;i<C;i++)
{
columntotal[i]=0;
}
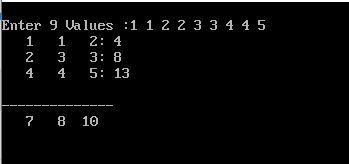
printf("\nEnter %d Values :",R*C);
for(i=0;i<R;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<C;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&mat[i][j]);
rowtotal[i] += mat[i][j]; //i for row
columntotal[j] += mat[i][j]; //j for column
}
}
//Printing Matrix and Totals
for(i=0;i<R;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<C;j++)
{
printf("%4d",mat[i][j]);
}
printf(": %d",rowtotal[i]); //Row Total Print
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n--------------\n");
for(i=0;i<C;i++)
{
printf("%4d",columntotal[i]);
}
getch();
}
- #define is a Macro that defines Constant Value for Entire Program
- In Double Dimension Array Index of element is (r,c) means
- (0,0) (0,1) (0,2)
- (1,0) (1,1) (1,2) …
